MemPro™ Leukotriene C4 synthase
Creative Biostructure provides custom MemPro™ gene-to-structure services for leukotriene C4 synthase.
Leukotriene C4 synthase (LTC4S), the pivotal enzyme for the biosynthesis of LTC4, is an 18-kDa integral nuclear membrane protein that belongs to a superfamily of membrane associated proteins in eicosanoid and glutathione metabolism (MAPEG). LTC4S catalyzes the key step that conjugates leukotriene A4 with reduced glutathione to form leukotriene C4. The LTC4S monomer has four transmembrane a-helices and forms a threefold symmetric trimer as a unit with functional domains across each interface.
Through site-directed mutagenesis, the key residues for the GSH-binding site and LTC4s activity have been identified. The bound GSH is in a U-shaped conformation, forming an intramolecular hydrogen bond between the backbone nitrogen atom of the glycyl moiety and an α-carboxyl oxygen of the γ-glutamyl moiety.
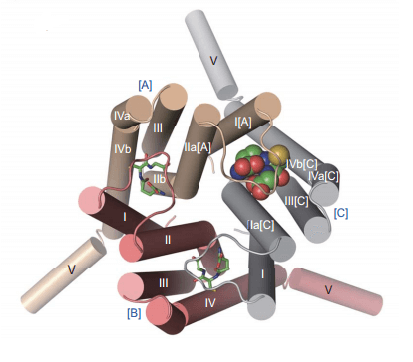 Figure 1. Structure of LTC4S: One GSH at the interface of [C] and [A] is shown in a space-filling model; the others are shown in a stick model.
Figure 1. Structure of LTC4S: One GSH at the interface of [C] and [A] is shown in a space-filling model; the others are shown in a stick model.
Cysteinyl leukotrienes are produced by activated mast cells, eosinophils and monocytes and elicit smooth muscle contractions at nanomolar concentrations in the respiratory tract and microcirculation. Cysteinyl leukotrienes are key mediators in inflammation and have an important role in acute and chronic inflammatory diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, in particular bronchial asthma. Hence, targeting the enzymes involved in the synthesis of these mediators can lead to the development of novel anti-inflammatory drugs. Drugs targeting cysteinyl leukotriene receptors have offered therapeutic opportunities in the medical treatment of asthma. However, no drugs have yet been developed targeting leukotriene C4 synthase. The understanding of the crystallized structure could lead to the design of new chemical candidates for inflammatory therapy.
Additional its crucial role in cardiovascular and respiratory systems, LTC4 stimulated skin fibroblasts to secrete factors that elicit keratinocyte proliferation. Deficient of LTC4S is related with atopic dermatitis that causes abnormal skin thicken. Some LTC4s inhibitors are under development to treat inflammatory diseases. 5-(5-methylene-4-oxo-4,5-dihydrothiazol-2-ylamino) isophthalic acid, an inhibitor of LTC4S, suppress LTC4 synthesis by interfere glutathione conjugation to the precursor LTA4, in both an enzyme assay and a whole-cell assay.
Creative Biostructure can provide custom MemPro™ Membrane Protein Gene-to-Structure services. Please click for more information.
Reference
Ago H, Okimoto N, Kanaoka Y, et al. A leukotriene C4 synthase inhibitor with the backbone of 5-(5-methylene-4-oxo-4, 5-dihydrothiazol-2-ylamino) isophthalic acid[J]. Journal of biochemistry, 2013, 153(5): 421-429.
Oyoshi M K, He R, Kanaoka Y, et al. Eosinophil-derived leukotriene C4 signals via type 2 cysteinyl leukotriene receptor to promote skin fibrosis in a mouse model of atopic dermatitis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2012, 109(13): 4992-4997.
S Devi N, Doble M. Leukotriene c4 synthase: upcoming drug target for inflammation[J]. Current drug targets, 2012, 13(8): 1114-1125.
