Structural Research of Rhodopsins
Rhodopsins, a class A member of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily 2, is found in optic rod photoreceptor cells of the retina and converts light signals into chemical signals that stimulate biological processes in the nervous system of humans and other vertebrates. It is the first GPCR to have its 3D structure resolved by X-ray crystallography, and its structure is an essential model for understanding the structural and functional characteristics of other GPCRs.
Overall structure of bovine rhodopsin
The first data on the 3D structure of bovine rhodopsin came from circular dichroism (CD) studies of sonicated disks and purified proteins, and FTIR data provided information on the rhodopsin helix. The structure shows that the bovine rhodopsin has a seven-transmembrane (7TM) helical core with three loop regions on both sides of the membrane. The N-terminus is located on the outer cell side and consists of a double-stranded β-fold extending from Gly4 to Pro11. Its C-terminus is located on the cytoplasmic side. It extends from residue Met309 at the C-terminus of helix 7 to the last residue of the receptor and has a short amphipathic helix perpendicular to helix 7 (helix 8).
Structural analysis of fungal rhodopsin
Researchers have crystallized the proton pumping type 1 rhodopsin, the light-driven proton pump LR, from the unicellular fungus Leptosphaeria maculans using an endocyclization method and demonstrated its high-resolution (2.2 Å) crystal structure. The structure shows that the retinal chromophore is fixed in an all-trans conformation, with the protonated retinal Schiff base (RSB) pointing extracellularly and providing hydrogen bonding to the w8 molecule. The LR consists of seven transmembrane helices TM1-TM7 connected by three intracellular (ICL 1-3) and three extracellular (ECL 1-3) loops, with the retinal chromophore covalently attached to K270 on TM7.
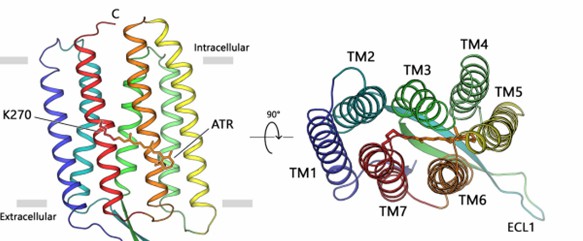 Figure 1. The overall architecture of fungal rhodopsin (LR). (Zabelskii D, et al., 2021)
Figure 1. The overall architecture of fungal rhodopsin (LR). (Zabelskii D, et al., 2021)
| Protein | Organism | Method | Resolution | PDB Entry ID |
| Light-driven proton pump LR (Mac) | Plenodomus lingam | X-ray diffraction | 2.2 Å | 7BMH |
| Viral rhodopsin OLPVRII | Organic Lake phycodnavirus | X-ray diffraction | 1.9 Å | 6SQG |
| Cyanorhodopsin (CyR) N2098R | Calothrix sp. NIES-2098 | X-ray diffraction | 2.65 Å | 6LM0 |
| The transmembrane domain of rhodopsin phosphodiesterase | Salpingoeca rosetta | X-ray diffraction | 2.6 Å | 7CJ3 |
| The transmembrane domain and linker region of rhodopsin phosphodiesterase | Salpingoeca rosetta | X-ray diffraction | 3.5 Å | 7D7Q |
| Microbial rhodopsin | Sphingomonas paucimobilis | X-ray diffraction | 2.8 Å | 8ANQ |
| Schizorhodopsin 4 | Asgard group archaeon | X-ray diffraction | 2.1 Å | 7E4G |
| Blue light-absorbing proteorhodopsin | uncultured bacterium | X-ray diffraction | 2.31 Å | 4JQ6 |
| Cyanorhodopsin (CyR) N4075R | Tolypothrix sp. NIES-4075 | X-ray diffraction | 1.9 Å | 6LM1 |
| Gloeobacter rhodopsin | Gloeobacter violaceus PCC 7421 | X-ray diffraction | 2 Å | 6NWD |
| Sensory rhodopsin II | Natronomonas pharaonis | X-ray diffraction | 2.1 Å | 1H68 |
| Sensory rhodopsin | Nostoc sp. PCC 7120 = FACHB-418 | X-ray diffraction | 2 Å | 1XIO |
| Green-light absorbing proteorhodopsin | uncultured Gammaproteobacteria bacterium | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 2.93 Å | 7B03 |
| Sensory Rhodopsin Determined | Nostoc sp. PCC 7120 = FACHB-418 | SOLID-STATE NMR | / | 2M3G |
| Rhodopsin | Exiguobacterium sibiricum | X-ray diffraction | 2.3 Å | 4HYJ |
| Viral rhodopsin OLPVR1 | Organic Lake phycodnavirus | X-ray diffraction | 1.4 Å | 7AKY |
| Xanthorhodopsin, a Light-Driven Ion Pump with Dual Chromophore | Salinibacter ruber | X-ray diffraction | 1.9 Å | 3DDL |
| Cruxrhodopsin-3 | Haloarcula vallismortis | X-ray diffraction | 2.3 Å | 4JR8 |
| Viral rhodopsins chimera O1O2 | Organic Lake phycodnavirus | X-ray diffraction | 1.96 Å | 7AKW |
| Archaerhodopsin-1 | Halorubrum ezzemoulense | X-ray diffraction | 3.4 Å | 1UAZ |
| The proton-pumping rhodopsin AR2 | Acetabularia acetabulum | X-ray diffraction | 3.2 Å | 3AM6 |
| Proteorhodopsin | uncultured marine gamma proteobacterium EBAC31A08 | SOLUTION NMR | / | 2L6X |
| The Closed State of Channelrhodopsin | Chlamydomonas reinhardtii | X-ray diffraction | 2.3 Å | 3UG9 |
| The light-driven chloride ion-pumping rhodopsin, ClP | Nonlabens marinus S1-08 | X-ray diffraction | 1.581 Å | 5B2N |
| Thermophilic rhodopsin | Thermus thermophilus JL-18 | X-ray diffraction | 2.8 Å | 5AZD |
| The red light-activated channelrhodopsin Chrimson. | Chlamydomonas noctigama | X-ray diffraction | 2.6 Å | 5ZHI |
| N24Q/C128T mutant of Channelrhodopsin 2 | Chlamydomonas reinhardtii | X-ray diffraction | 2.7 Å | 6EIG |
| Proton pump MAR rhodopsin pressurized with krypton | Candidatus Actinomarina minuta | X-ray diffraction | 2.25 Å | 7Q37 |
| Halorhodopsin, a light-driven chloride pump | Halobacterium salinarum | X-ray diffraction | 1.8 Å | 1E12 |
| wild-type Channelrhodopsin 2 | Chlamydomonas reinhardtii | X-ray diffraction | 2.39 Å | 6EID |
Table 1. Structural research of rhodopsins.
Creative Biostructure is a renowned entity in structural biology, providing cutting-edge structural analysis services. We offer X-ray crystallography, cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy technologies to unravel the molecular mechanisms of photoreception and signaling of rhodopsin in the visual system.
Our clients can take advantage of our comprehensive structural analysis services, starting from the initial stages of protein expression and purification, all the way to the final stages of structure determination. Our unwavering commitment to delivering high-quality, accurate, and timely structural analysis results continues to earn us rave reviews from our clients. We welcome you to contact us for more details.
References
- Zabelskii D, et al. Structure-based insights into evolution of rhodopsins. Commun Biol. 2021. 4(1): 821.
- Zhou XE, et al. Structure and activation of rhodopsin.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012. 33(3): 291-299.