Structural Research of Electron Transport Chain Supercomplexes
The enzymes within the mitochondrial electron transport chain play a critical role in cellular metabolism. Although they are active when isolated, they form supercomplexes in vivo, the exact function of which is currently under debate.
Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) has significantly advanced structural biology, providing near-atomic resolution visualization of large macromolecular complexes. Recently, cryo-EM was used to visualize a respiratory supercomplex from Mycobacterium smegmatis, a bacterium causing tuberculosis. The structure consists of 20 subunits that associate to form the complex, including a CIII dimer, flanked by individual CIV subunits. Fused c-type cytochrome domains bridge and mediate electron transfer from CIII to CIV. Additionally, the structure revealed three previously unknown subunits, contributing to the supercomplex stability, and the presence of superoxide dismutase (SOD), responsible for the detoxification of superoxide formed by CIII.
In mammals, there are three types of supercomplexes, CICIII2, CIII2CIV1-2 and CICIII2CIV (respirasome), which differ in their organizations. Recently, the structures of mammalian (ovine and mouse) CIII2CIV and its assembly intermediates in distinct conformations were presented. The assembly of CIII2CIV from the CIII2 precursor to the final CIII2CIV conformation was elucidated. These findings provide valuable insights into the assembly and organization of the respiratory supercomplexes.
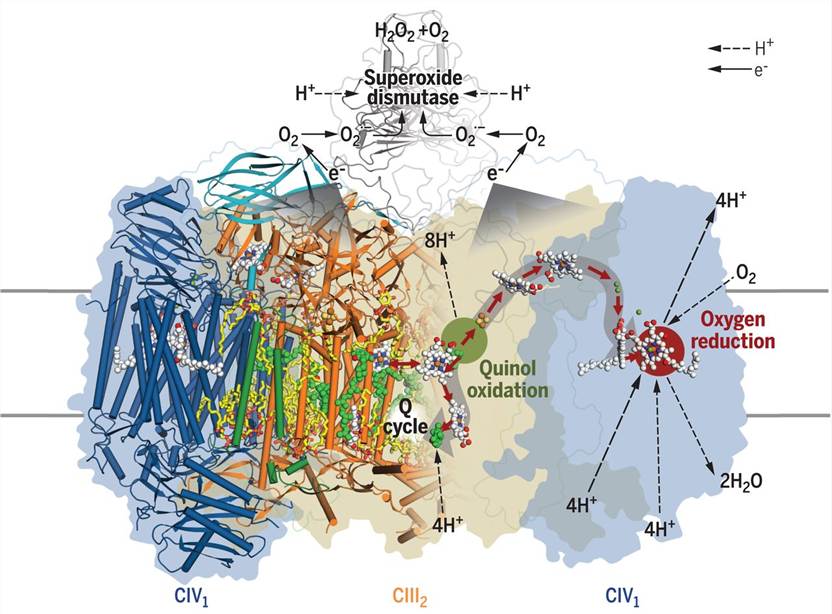 Figure 1. Structure of mycobacterial respiratory supercomplex CIII2CIV2SOD2. (Gong H, et al., 2018)
Figure 1. Structure of mycobacterial respiratory supercomplex CIII2CIV2SOD2. (Gong H, et al., 2018)
| Protein | Organism | Method | Resolution | PDB Entry ID |
| Electron Transport Chain (ETC) Super Complex comprised of ETC complexes I, III, and IV, tight respirasome | Ovis aries | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 5.80 Å | 5J4Z |
| Electron Transport Chain (ETC) Super Complex I+III2, closed class | Ovis aries | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 4.20 Å | 6QBX |
| Electron Transport Chain (ETC) Super Complex comprised of ETC complexes I, III, and IV | Sus scrofa | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 5.40 Å | 5GPN |
| Electron Transport Chain (ETC) Super Complex I1III2IV1 | Sus scrofa | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 4.00 Å | 5GUP |
| Respiratory supercomplex CIII2CIV2SOD2 | Mycolicibacterium smegmatis | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.50 Å | 6ADQ |
| Respiratory supercomplex CIII2CIV2 (expressed in Mycolicibacterium smegmatis) | Mycolicibacterium smegmatis | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.30 Å | 6HWH |
| Respiratory supercomplex CIII2CIV2 with bound Telacebec (Q203) | Mycolicibacterium smegmatis | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.00 Å | 7RH7 |
| Electron Transport Chain (ETC) Super Complex III2IV | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.23 Å | 6GIQ |
| Rcf1 protein involved in electron chain super-complex formation (expressed in E. coli) | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Solution NMR | / | 5NF8 |
| Electron Transport Chain (ETC) Super Complex III2IV2 (expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae) | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.35 Å | 6HU9 |
| III2-IV(5B)1 respiratory supercomplex (expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae) | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.29 Å | 6T15 |
| Respiratory supercomplex Factor 2 (expressed in E. coli) | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Solution NMR | / | 6LUL |
| CIII2/CIV respiratory supercomplex | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.17 Å | 6YMX |
| Respiratory supercomplex III2-IV | Vigna radiata | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.80 Å | 7JRP |
| Respiratory supercomplex III2-IV. CIII2 (expressed in Rhodobacter capsulatus) | Rhodobacter capsulatus | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.30 Å | 6XI0 |
| Electron Transport Chain (ETC) hybrid Super Complex comprised of M. tuberculosis complexIII and M. smegmatis complexIV | Mycolicibacterium smegmatis | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 2.68 Å | 7E1V |
| ETC Super Complex comprised of ETC complexes CIII2CIV, intermediate locked conformation | Mus musculus | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.60 Å | 7O3E |
| III2-IV2 respiratory supercomplex (expressed in Corynebacterium glutamicum) | Corynebacterium glutamicum | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 2.90 Å | 7Q21 |
| III2-IV2 respiratory supercomplex, native (expressed in Corynebacterium glutamicum) | Corynebacterium glutamicum | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.10 Å | 7QHO |
| Respiratory chain super-complex CI+III2 | Tetrahymena thermophila | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 2.60 Å | 7TGH |
| Electron Transport Chain (ETC) Super Complex, optimized supercomplex state1 | Bos taurus | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 5.00 Å | 7DGQ |
Table 1. Structural Research of Electron Transport Chain Supercomplexes.
The increasing interest in the structure and function of supercomplexes has led to a demand for high-quality structural analysis services. Cryo-EM is a powerful technique for visualizing these large macromolecular complexes, but it requires specialized expertise and equipment. Creative Biostructure is a leading provider of protein structural analysis services, offering cryo-EM, X-ray crystallography, and NMR spectroscopy services for a wide range of biological macromolecules, such as electron transport chain supercomplexes. We provide comprehensive cryo-EM services, from sample preparation to data collection and processing, to generate high-resolution structures of complex biological systems.
If you are keen on delving into the structural research of supercomplexes and want to know more about the services we provide, please feel free to contact us. Our team is available round the clock to address your research requirements and offer optimal solutions for your project.
References
- Gong H, et al. An electron transfer path connects subunits of a mycobacterial respiratory supercomplex. Science. 2018, 362(6418): eaat8923.
- Vercellino I, Sazanov L A. Structure and assembly of the mammalian mitochondrial supercomplex CIII2CIV. Nature. 2021, 598(7880): 364-367.
- Zhou L, et al. Structures of Tetrahymena's respiratory chain reveal the diversity of eukaryotic core metabolism. Science. 2022, 376(6595): 831-839.