What is Exosome Microbiomics Analysis?
Exosome microbiomics analysis is a relatively complex and cutting-edge field of research, combining techniques and methods from both exosome research and microbiomics. Microbiomics focuses on microbial communities and their interactions with the host or environment. In recent years, researchers have explored this field regarding exosome-microbe interactions and the application of exosomes in the study of microbe-related diseases.
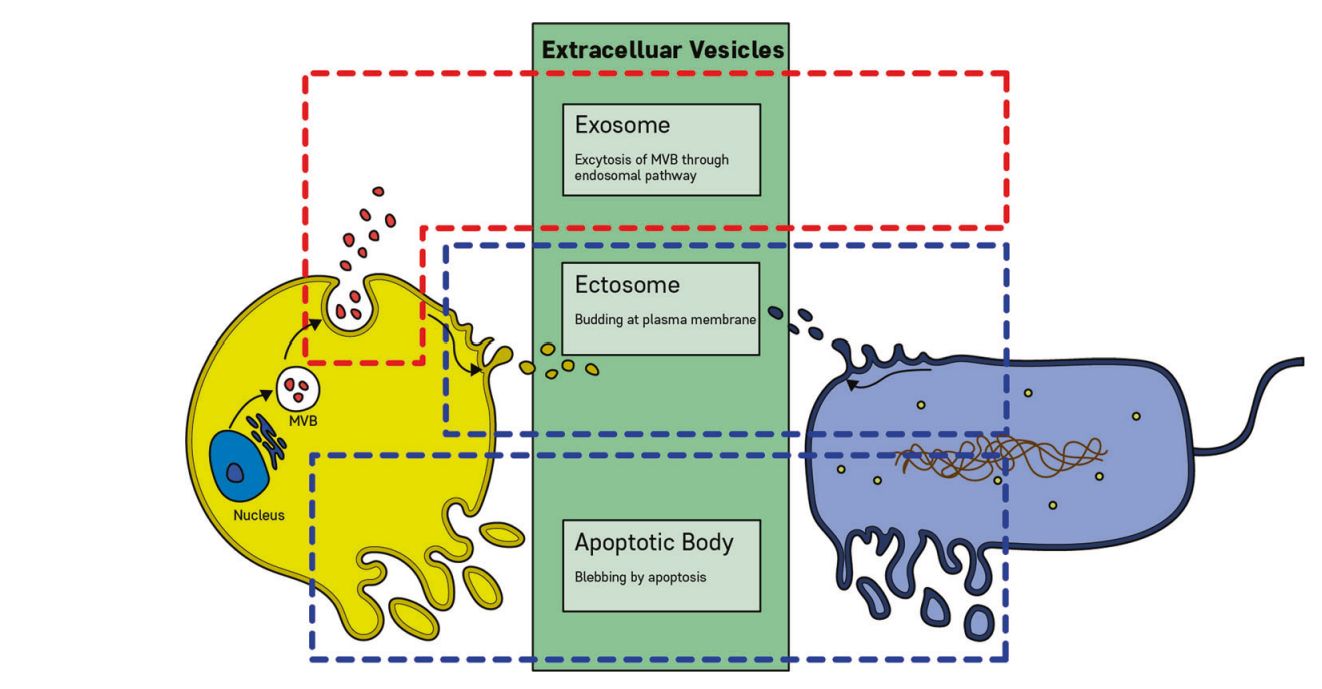 Figure 1. Extracellular vesicles from eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. (Yang J, et al., 2022)
Figure 1. Extracellular vesicles from eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. (Yang J, et al., 2022)
Research Directions for Exosomes in Microbiomics
- Microbial-derived Exosomes
Although exosomes are mainly released by cells, microorganisms (e.g., bacteria, fungi, etc.) can also produce similar structures. These structures may have similar functions to exosomes, such as information transfer and material exchange. These structures produced by microorganisms are often referred to as outer membrane vesicles (OMVs).
- Exosome-microbe Interactions
Exosomes play an important role in host-microbe interactions. For example, exosomes released by host cells can carry antimicrobial peptides, immunomodulatory molecules, etc. in response to microbial infections. At the same time, OMVs of microbial origin can also carry toxins, enzymes, etc., which can affect host cells.
Steps in Exosome Microbiomics Research
1. Extraction and Purification of Exosomes
Isolation of exosomes from biological samples such as cell culture supernatants, blood, and urine is performed using a variety of methods, including density gradient centrifugation, volumetric exclusion, immunoadsorption, and polymer precipitation-based methods.
After extraction, exosomes need to be further purified to remove impurities such as proteins and cellular debris.
2. Characterization of Exosomes
Characterization of exosomes usually includes morphological identification (e.g., transmission electron microscopy TEM), particle size distribution analysis (e.g., nanoparticle tracking analysis NTA), and Detection of protein markers (e.g. Western blot for CD63, CD9, and CD81).
3. Microbiome Analysis
Nucleic Acid Extraction - Extraction of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) from purified exosomes that may contain genetic information about the microorganism.
Sequencing - Sequencing of extracted nucleic acids using high-throughput sequencing technologies (e.g., 16S rRNA gene sequencing and macro-genome sequencing) to obtain information on microbial composition and diversity.
Data Analysis - Sequencing data are processed and analyzed through bioinformatics methods to identify microbial species, abundance, function, etc., and to explore their relationship with the host or disease state.
4. Validation and Interpretation of Results
The results of the analysis are validated to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the results. Interpret potential links between the exosome microbiome and host health, disease state, or treatment response.
Exosomes in the Study of Microbe-Associated Diseases
Disease Diagnosis - Biomolecules (e.g., proteins, nucleic acids, etc.) in exosomes can reflect cellular states and pathological changes, and thus have potential as biomarkers. In microbe-associated diseases, specific molecules in exosomes may be closely related to the onset and progression of the disease, thus becoming potential markers for disease diagnosis.
Disease Mechanism Studies - By analyzing biomolecules in exosomes, it is possible to reveal the mechanisms of interactions between microbes and host cells, and how these interactions affect the onset and progression of disease. This is important for understanding disease mechanisms and developing new therapeutic strategies.
Therapeutic Potential - Exosomes have the potential to serve as drug carriers that can carry therapeutic molecules for targeted delivery to disease sites. In the treatment of microbe-associated diseases, exosomes may become a new therapeutic tool to enhance host resistance to microbial infections by carrying antimicrobial peptides, immunomodulatory molecules, etc.
Research Cases
- Gut Microbe-derived Exosomes Have a Potential Role in Metabolism-Associated Fatty Liver Disease
The incidence of metabolism-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is increasing worldwide. Most previous studies have focused on exosomes of adipocyte and hepatocyte origin, while the role and molecular mechanisms of exosomes of microbial origin in MAFLD have received little attention. Therefore, researchers searched the database for studies to elucidate the link between microbial-derived exosomes and the pathogenesis of MAFLD, mainly in terms of intestinal barrier, insulin resistance, inflammatory response, lipid metabolism, and hepatic fibrosis, to support clinical protocols and innovative drug development.
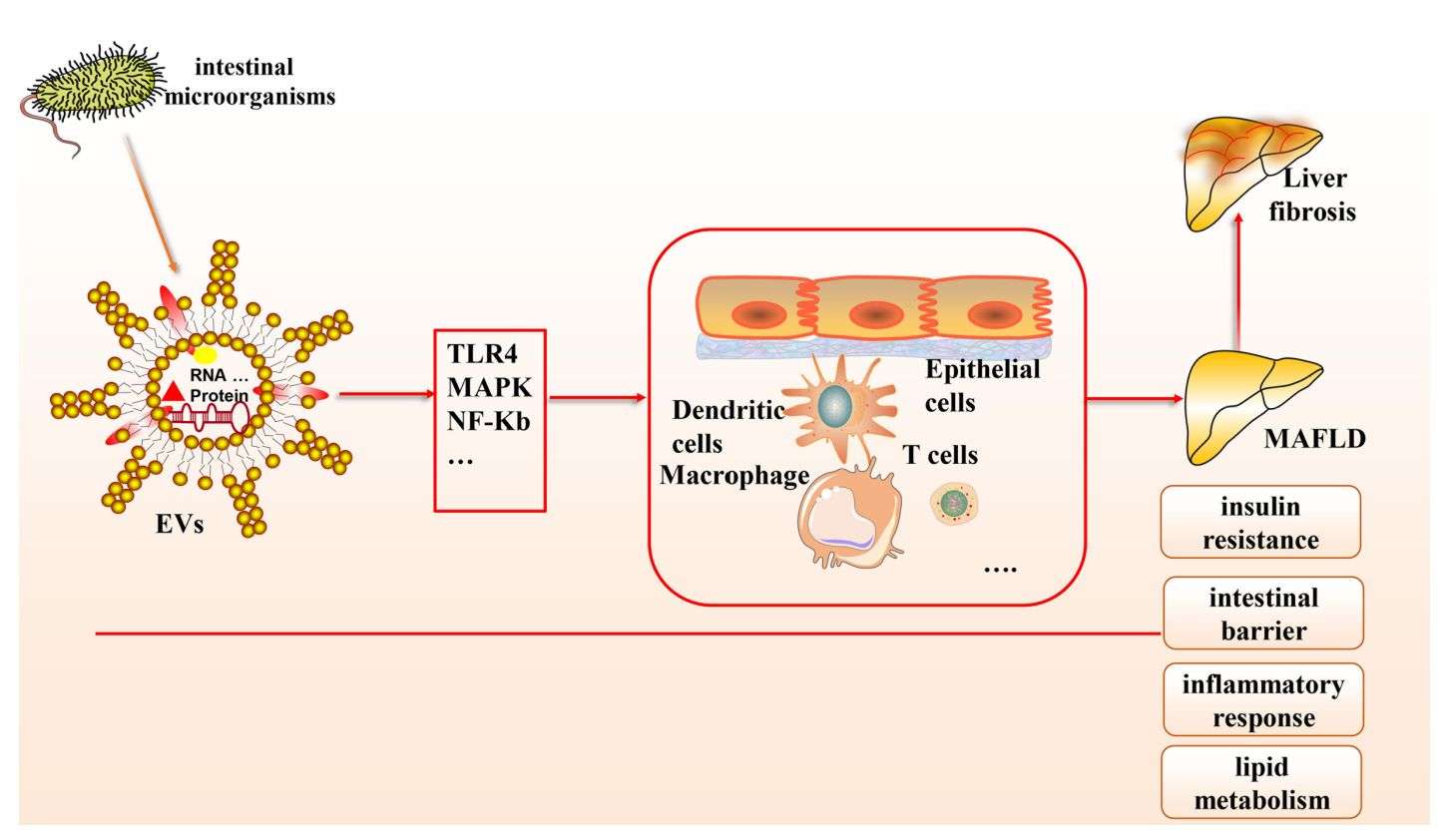 Figure 2. Association of gut microbe-derived exosomes with MAFLD. (Zhang B, et al., 2022)
Figure 2. Association of gut microbe-derived exosomes with MAFLD. (Zhang B, et al., 2022)
- Analysis of the Gut Microbiome Using Extracellular Vesicles in the Urine of Colorectal Cancer Patients
Researchers used extracellular vesicles (EVs) in the urine of colorectal cancer (CRC) patients to assess the gut microbiome. They isolated EVs from the urine of CRC patients and healthy controls and extracted DNA, then analyzed the bacterial composition using next-generation sequencing of 16S rRNA. The study found differences in certain microbiomes in the CRC group compared to the control group. The microbial characterization of EVs in urine could be a potential biomarker for the diagnosis of CRC.
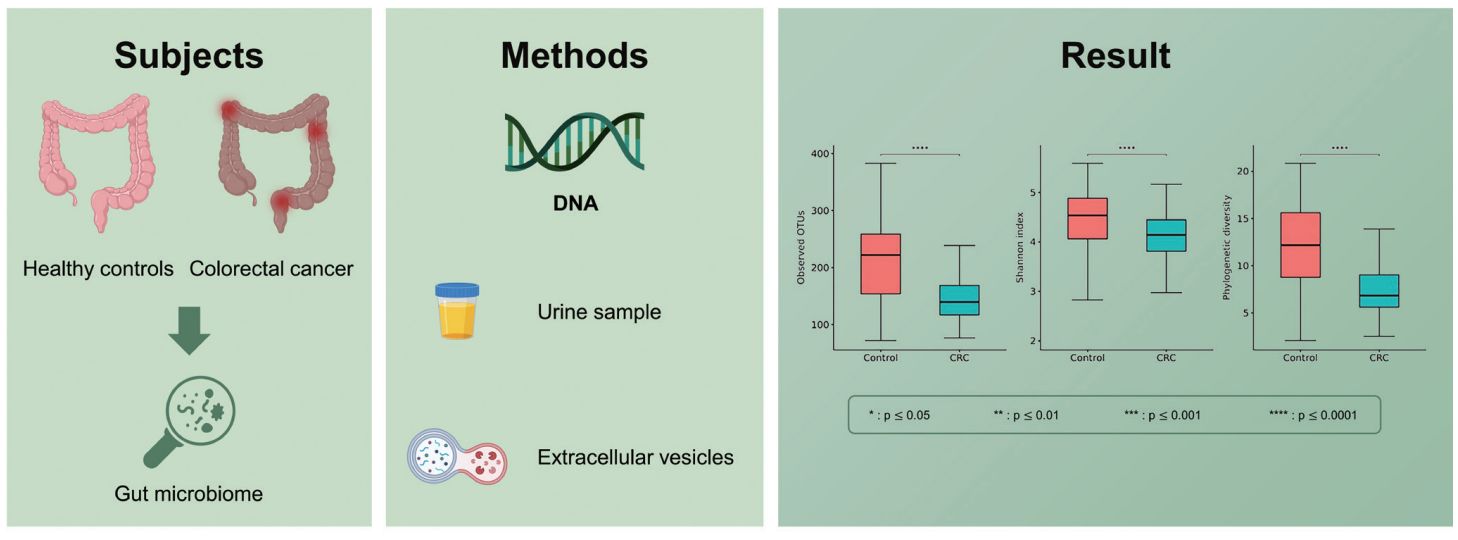 Figure 3. Analysis of the gut microbiome using EVs in the urine of colorectal cancer patients. (Yoon H, et al., 2023)
Figure 3. Analysis of the gut microbiome using EVs in the urine of colorectal cancer patients. (Yoon H, et al., 2023)
Today We Offer
Exosome microbiome analysis is a research field full of challenges and opportunities. As technology continues to advance and methods are refined, it is reasonable to believe that this field will play an important role in the diagnosis, treatment, and mechanistic studies of microbe-related diseases.
Being at the forefront of exosome research, Creative Biostructure helps clients explore the exciting world of exosome microbiomics. We offer a comprehensive range of services and products to help researchers delve into the intricate interactions between exosomes and the microbiome. From exosome isolation and characterization to cutting-edge sequencing and histological analysis, we provide the tools and expertise to unravel exosome-based microbial signatures. Our mission is to unlock the potential of exosome microbiomics to improve our clients' understanding of microbiome-host interactions, disease pathogenesis, and the development of novel diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Please feel free to contact us for more information.
References
- Yang J, et al. A new horizon of precision medicine: combination of the microbiome and extracellular vesicles. Exp Mol Med. 2022. 54(4): 466-482.
- Zhang B, et al. The Potential Role of Gut Microbial-Derived Exosomes in Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: Implications for Treatment. Front Immunol. 2022. 13: 893617.
- Yoon H, et al. Analysis of the gut microbiome using extracellular vesicles in the urine of patients with colorectal cancer. Korean J Intern Med. 2023. 38(1): 27-38.