Structural Research of Membrane-Associated Proteins in Eicosanoid and Glutathione Metabolism (MAPEG)
The membrane-associated proteins in eicosonic acid and glutathione metabolism (MAPEG) are a widespread mammalian superfamily. MAPEG is involved in the biological transformation of electrophilic substances and is also involved in pain, fever and inflammation caused by arachidonic acid.
Research Progress of MGST1 Structure
MGST1 belongs to the MAPEG family. The structure of MGST1 is determined by the electron crystal method. The image amplitude and phase data can be obtained at 3 Å resolution. MGST1 data were recorded with Jeol 3000SFF(Electron Microscope Liquid Helium Cooled Sample Station). Two kinds of crystals are obtained, with two-sided plane groups of hexagonal p6 and orthogonal bodies p22121, and the symmetric auto-modifiers are composed of three repeats of a four-helix transmembrane bundle, with the largest extracellular domain connecting the first and second helices and a short proline-rich ring between the third and fourth helices on the same side.
Research Progress of LTC4S Structure
LTC4S is also a well-known member of the MAPEG family. The localization pathway of the protruding fifth helix of the LTC4S four-helical membrane localization bundle in the lipid bilayer was observed by X-ray. Studying the interaction of MAPEGs with substrates or inhibitors in the lipid environment will help to understand the relationship between their structure and function. This could be important for drug development.
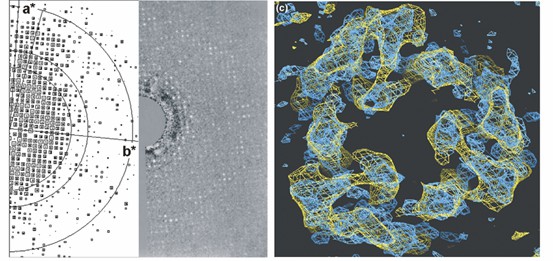 Figure 1. From rat liver microsomes to 3D maps of MGST1. (Hebert, et al., 2007)
Figure 1. From rat liver microsomes to 3D maps of MGST1. (Hebert, et al., 2007)
| Protein | Organism | Method | Resolution | PDB Entry ID |
| Human FLAP with MK-591 | Homo sapiens | X-ray diffraction | 4.25 Å | 2Q7M |
| Human FLAP with an iodinated analog of MK-591 | Homo sapiens | X-ray diffraction | 4.00 Å | 2Q7R |
| FLAP bound to DG-031 | Homo sapiens | X-ray diffraction | 2.37 Å | 6VGC |
| Human Leukotriene C4 synthase | Homo sapiens | X-ray diffraction | 2.00 Å | 2UUI |
| Leukotriene C4 Synthase in complex with substrate glutathione | Homo sapiens | X-ray diffraction | 2.15 Å | 2UUH |
| C4 synthase in complex with dodecyl-beta-D-selenomaltoside | Homo sapiens | X-ray diffraction | 3.20 Å | 3B29 |
| Leukotriene C4 synthase in complex with glutathione sulfonate | Homo sapiens | X-ray diffraction | 2.90 Å | 3HKK |
| LTC4 synthase in GSH complex form | Mus musculus | X-ray diffraction | 2.70 Å | 4NTB |
| LTBP1 Y114A mutant in complex with leukotriene C4 | Rhodnius prolixus | X-ray diffraction | 1.28 Å | 5H9N |
| Microsomal glutathione transferase 1 | Rattus norvegicus | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.50 Å | 5I9K |
| Human PS-1 GSH-analog complex | Homo sapiens | X-ray diffraction | 1.95 Å | 4AL1 |
| Microsomal glutathione transferase 1 in complex with glutathione | Rattus norvegicus | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.20 Å | 2H8A |
| Microsomal glutathione transferase 1 in complex with Meisenheimer complex | Rattus norvegicus | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.50 Å | 5IA9 |
| Human microsomal glutathione S-transferase 2 | Homo sapiens | X-ray diffraction | 2.498 Å | 6SSS |
| Human microsomal glutathione S-transferase 2 in complex with an inhibitor glutathione sulfonic acid | Homo sapiens | X-ray diffraction | 3.00 Å | 6SSW |
| Human microsomal prostaglandin E synthase 1 | Homo sapiens | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.50 Å | 3DWW |
| Human integral membrane enzyme | Homo sapiens | X-ray diffraction | 2.08 Å | 4BPM |
| Human PS-1 | Homo sapiens | X-ray diffraction | 1.16 Å | 4AL0 |
Table 1. Structural research of membrane-associated proteins in eicosanoid and glutathione metabolism (MAPEG).
Creative Biostructure uses cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and X-ray crystallography to investigate membrane-associated proteins in eicosanoid and glutathione metabolism (MAPEG). The obtained cryo-electron microscope structure is conducive to the study of its function and role in disease and could help the development of targeted drugs.
We have long been committed to the study of structural biology and membrane proteins. Our experts have extensive experience in the determination of membrane protein structures using single particle analysis (SPA).
In addition to the structural determination of membrane proteins, we can accurately analyze other biomolecules, including but not limited to ribosomes, nucleic acids, small proteins, protein complexes, protein-ligand complexes, and viruses. If you are interested in our services, please contact us for more details.
References
- Hebert, et al. "The structure of membrane associated proteins in eicosanoid and glutathione metabolism as determined by electron crystallography." Current opinion in structural biology, 2007: 396-404.
- Jakobsson PJ, et al. Membrane-associated proteins in eicosanoid and glutathione metabolism (MAPEG). A widespread protein superfamily. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000,161(2):20-24.
- Jakobsson PJ, et al. Common structural features of MAPEG - a widespread superfamily of membrane associated proteins with highly divergent functions in eicosanoid and glutathione metabolism. Protein Science: a Publication of the Protein Society. 1999, 8(3):689-692.
- Bresell A, et al. Bioinformatic and enzymatic characterization of the MAPEG superfamily. FEBS J. 2005, 272(7):1688-1703.