Mempro™ Proteoliposomes
Creative Biostructure is a specialized company in providing comprehensive products and services of membrane proteins to numerous research institutes and companies for many decades. One of the major barriers in therapy is the poor delivery system which is inconvenient and ineffective for treatments. Mempro™ Liposome Technology is a well established technique to develop novel pharmaceutical formulations and vaccines, and these encapsulated durgs can be treated topically, orally, or through parenteral routes.
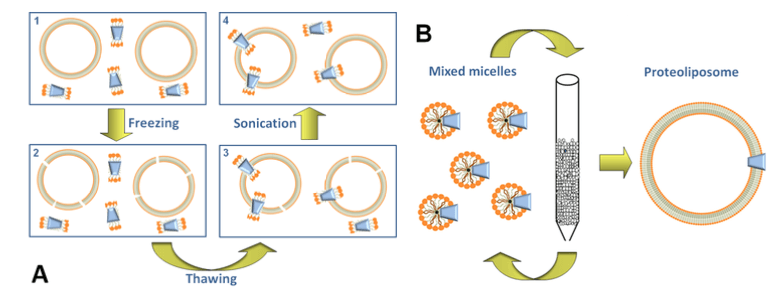 Figure 1. Schemed representation of preparation of proteoliposome. Freeze-thaw sonication is consist of the following four steps: (1) mixture of liposome, protein and detergent; (2) freezing of the mixture; (3) Protein which solubilized in detergent has inserted into the membrane by slow thawing; (4) mild sonication facilitates the sealing of proteoliposomes. (M. Scalise, et al., 2016)
Figure 1. Schemed representation of preparation of proteoliposome. Freeze-thaw sonication is consist of the following four steps: (1) mixture of liposome, protein and detergent; (2) freezing of the mixture; (3) Protein which solubilized in detergent has inserted into the membrane by slow thawing; (4) mild sonication facilitates the sealing of proteoliposomes. (M. Scalise, et al., 2016)
The liposomes in which the proteins have been inserted are known as proteoliposomes. The use of proteoliposomes with therapeutic membrane proteins allow biologically active proteins to transport through the cell membranes. One of the chanllenges to apply this powerful delivery system is the high-quality production of membrane proteins since they are difficult to purify, and we have develop Mempro™ Membrane Protein platform to solve this problem. As for formation of proteoliposomes, Creative Biostructure has adopted methods based on the classic protocols of hydration or electroformation with a careful execution. In case of the proteins denatured, gentle dehydration process has been applied. Furthermore, chemicals compounds like carbohydrates or ethylene glycol are able to prevent complete dehydration. The freeze-thaw-sonication method was also pointed out in Figure 1, and this method is well compatible with our bacterial cell-free expression system.
Proteoliposomes have been used as a powerful tool to study membrane transporters (especially the ABC transporters) in a native-like environment. Metabolite exchanges between cells are based on the functions of transport systems. In order to better characterize the function, kinetics and regulation of transporters, we can adopt proteoliposomes as an model membrane.
In recent years, Creative Biostructure has developed a variety of novel liposomes such as stimuli-sensitive liposomes which are able to respond to different environmental factors including pH, magnetism, light, and temperature, leading to triggered release of bioactive molecules. For example, infectious bacteria secrete some proteinases which can disrupt the protein being incorporated into the membrane of proteoliposomes, triggering the release of antimicrobial agents. To put it differently, the antimicrobial agents encapsulated in proteoliposomes will only be released when the proteoliposomes encountered the targeted infective bacteria which could secrete the proteinase. The released antimicrobial agents will then perform their activity rapidly and locally.
Creative Biostructure is the best formulator and manufacturer of functional liposomes, and we can help you evaluate intellectual property, plan and perform research and develepment projects based on our advanced Mempro™ Liposome Technology. Please feel free to contact us for a detailed quote.
References:
K. S. Horger, et al. (2015). Hydrogel-assisted functional reconstitution of human P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) in giant liposomes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1848: 643–653.
M. Bolean, et al. (2015). Proteoliposomes with the ability to transport Ca2+ into the vesicles and hydrolyze phosphosubstrates on their surface. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 584: 79-89.
M. Scalise, et al. (2013). Proteoliposomes as Tool for Assaying Membrane Transporter Functions and Interactions with Xenobiotics. Pharmaceutics, 5: 472-497.