Mempro™ Long Circulating Liposomes
Creative Biostructure has developed an innovative and comprehensive Mempro™ Liposome platform to provide various cuostom products and services for our clients from all over the world. Creative Biostructure has applied Mempro™ Liposome Technology to develop novel Mempro™ Long Circulating Liposomes for better delivery.
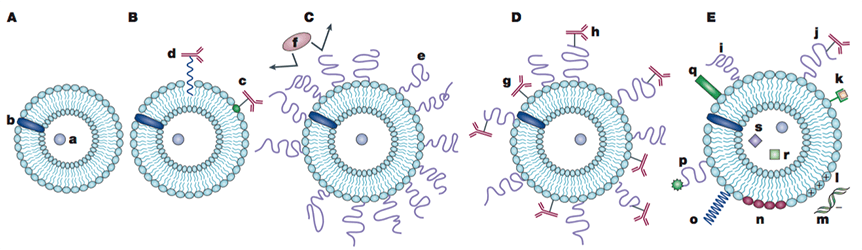 Figure 1. Novel functional liposomes. Traditional liposomes (A); Antibody-targeted immunoliposome (B); Long circulating liposomes with protective polymers such as PEG (C); Long-circulating immunoliposome (D); New-generation liposomes with different modifications (E). (V. P. Torchilin, 2005)
Figure 1. Novel functional liposomes. Traditional liposomes (A); Antibody-targeted immunoliposome (B); Long circulating liposomes with protective polymers such as PEG (C); Long-circulating immunoliposome (D); New-generation liposomes with different modifications (E). (V. P. Torchilin, 2005)
Liposomes are self-closed spherical vesicles created by different lipids with bilayer structure. Both hydrophilic and lipophilic drugs can be incorporated into liposomes which act as biocompatible carriers, however, one major drawback of the application of liposomes in drug delivery and gene/cancer therapy is the fast elimination in the blood. Long circulating liposomes are one kind of liposomes which are modified with certain polymers to achieve much longer staying for liposomes in the blood.
Mempro™ Long Circulating Liposomes have been used to increase the duration of the encapsulated drugs because they can maintain drug levels, decrease the toxicity, and reduce side effects of various drugs. Mempro™ Long Circulating Liposomes have also shown non-specific accumulation in infarcted areas and tumors tissues by the EPR (enhanced permeability and retention) effect. Creative Biostructure is able to perform various modification on the surfaces of Mempro™ Long Circulating Liposomes with specific attachments for targeting.
Mempro™ Long Circulating Liposomes have a lot of advantages such as non-saturable, dose-independent, and increased bioavailability. A variety of strategies have been developed to prepare long circulation liposomes in vivo. One of the most applied methods is to coat the surface of liposomes with polymers which are inert and biocompatible such as PEG. PEG forms a protective layer which can slow down liposome recognition and clearance. The protective polymers have great flexibility, avoiding impermeable layer formed by a large number of surface-grafted polymer molecules.
Mempro™ Long Circulating Liposomes have been also used in cancer chemotherapy since they are promising carriers for imaging agents. Though PEG liposomes are thought to be biologically inert previously, they recently showed the ability to induce specific side reactions based on the activation of the complement system. To maximumly functionalize novel liposomes, Creative Biostructure has recently attempted to combine the advantages of long-circulating liposomes, pH-sensitive liposomes and immunoliposomes together in one preparation. Attaching the targeting ligands with a PEG spacer arm is favorable to deliver better selectivity of long-circulating liposomes, reducing steric hindrance of targeted binding since the ligand is outstretched of the PEG brush.
Besides Mempro™ Long Circulating Liposomes, Creative Biostructure is also expertized in development and production of other functional liposomes. Please feel free to contact us for a detailed quote.
References:
H. Xu, et al. (2016). Development of Long-Circulating pH-Sensitive Liposomes to Circumvent Gemcitabine Resistance in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Pharm. Res., 33: 1628–1637.
V. Kannan, et al. (2014). Optimization of drug loading to improve physical stability of paclitaxel-loaded long-circulating liposomes. J. Liposome. Res., 25(4): 308–315.
V. P. Torchilin. (2005). Recent advances with liposomes as pharmaceutical carriers. Nature Reviews | Drug Discovery, 4: 145-160.